Geometry
Glossary - P
- Parallelogram:
- see
quadrilateral see
congruent
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/paralgra.gif)
- Parallelepiped:
- a prism whose bases are parallelograms
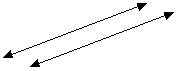
- Parallel Line:
- two lines, which lie
in the same plane and are at all points equidistant from each other
- Parallel Planes:
- two planes that are
at all points equidistant from each other
- Pentagon:
- a polygon with five sides
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/pentagon.gif)
-
-
- Perimeter:
- the distance around
any object; for a polygon, the perimeter
is the sum of the measures of the sides; the circumference of a circle is analogous to perimeter;
measurement of perimeter is expressed in linear units
- Perpendicular bisector:
- a line or segment,
which intersects a segment at its midpoint to form a right angle
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/perpbisc.gif)
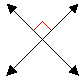
- Perpendicular lines:
- two lines meeting to
form right angles
- Pi (
 ): ):
- an irrational number
that represents the ratio of the circumference of a given circle to its diameter
- Plane ( Undefined
Term ):
- can be described as
an infinite, flat, two-dimensional surface that is named by a script
capital letter
- Point ( Undefined
Term ):
- can be described as
a zero-dimensional "dot" that is named using a capital letter
- Point-slope form
of a linear equation:
- y-y1 =m(x-x1 )
- Polygon:
- a closed curve
formed only by line segments that meet at their endpoints (called
vertices)
see also: simple
closed curve
- Polygonal region:
- the union of a polygon and its interior
- Polyhedron:
- literally "many faces";
it is the union of four or more polygons meeting at their edges and enclosing a single space
-
- Postulate:
- a statement accepted
as true without proof; synonymous to an axiom
- Prism:
- a polyhedron with two congruent parallel bases
and lateral faces that are parallelograms;
a prism is named by the shape of its bases; for example, a triangular
prism has congruent triangles for its bases
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/prism.gif)
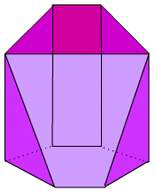
- Prismatoid:
- a polyhedron resembling
a prism (two bases in parallel planes);
however, its bases need not be congruent,
nor even the same type of polygon; all of its vertices in two parallel
planes and its lateral faces are quadrilaterals and/or triangles
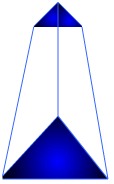
- Prismoid:
- a prismatoid with two
similar, but not congruent, bases;
its lateral faces are trapezoids
- Protractor:
- an instrument
used to measure an angle; typical scale units are degrees
- Pyramid:
- a polyhedron with one base and triangular lateral faces; A pyramid "comes to
a point" and is named for the shape of its base - below is pictured
a pentagonal pyramid
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/pyramid.gif)
- Pythagorean Theorem:
- in a right
triangle, the sum of the squares of the measure of the legs
of the triangle are equal to the square of the measure of the hypotenuse
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/pythago.gif)
|
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/paralgra.gif)

![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/pentagon.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/perpbisc.gif)

![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/prism.gif)


![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/pyramid.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/pythago.gif)





