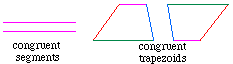
Geometry
Glossary - C
|
||||||||||
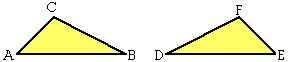 |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
- Conic:
- an adjective describing any surface which has one base connected to a point, not in the plane of the base, by a smooth surface or triangular lateral faces; both cones and pyramids are conical
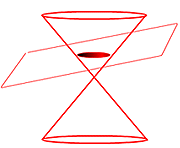
- Conic Section:
- the intersection of a plane and double cone (two congruent right cones aligned tip to tip with bases parallel); the conic sections are ellipse, circle, hyperbola, and parabola
- Conjecture:
- a statement proposing that some observed characteristic might be true in all cases; further testing and observation may validate or disprove the conjecture (also called supposition or hypothesis)
- Conjunction:
- two statements joined by the word "and;" the conjunction is true if both statements are true
- Construct:
- to draw a geometrical figure so as to fulfill given conditions
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/convex.gif)
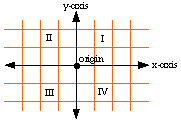
- Coordinate Plane:
- the grid formed by vertical and horizontal number lines that intersect at zero; also called the Cartesian Plane (named for Rene Descartes, its founder)
- Coordinates:
- the number assigned to the graph of a point on a number line;
OR the ordered pair (x,
y), which describes the location of a point in the xy-plane;
OR the ordered triple (x, y, z), which describes the location of
a point in space
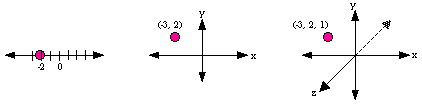
- Coplanar:
- points or lines that lie in the same plane
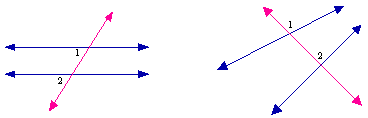
- Corresponding angles:
- these pairs occur when two lines are intersected by a transversal; they occupy the same position with respect to the transversal and the original lines
- Cosecant:
- Cosine:
- in a right triangle, the ratio of the measure of the adjacent side to the measure of the hypotenuse
- a trigonometric function equal to the x-coordinate of the point of intersection of the terminal ray of an angle in standard position with the unit circle
- Cotangent:
- Coterminal angles:
- angles are coterminal if they share the same terminal ray and are in standard position
- Corresponding angles:
- angles that are formed on the same side of a transversal
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/corrangl.gif)
- Cylinder:
- the surface of a cylindric solid whose parallel bases are congruent circles
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/circcyl.gif)
Adapted with permission from NCS Pearson, Inc. (Educational Structures) Copyright © 2000.



![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/centangl.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/chord.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/circle.gif)

![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/circumpo.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/concave.gif)