Geometry
Glossary - R
- Radian:
- a unit of angular measure
equal to the measure of a central angle intercepting a one-unit long arc on the
unit circle
- Radical:
- a square
root
- Radicand:
- the number under
the radical sign
- Radius:
- a line segment
that joins the center of the circle to a point on the circle
- also, a line segment that joins the center
of a regular polygon to a vertex of
the polygon
- Ray:
- "half of a line;" the
union of a segment and all the points (on the line containing the
segment) beyond one of the endpoints of the segment
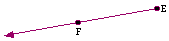
- Rectangle:
- a quadrilateral with four right angles (a rectangle is
a special kind of parallelogram)
- Rectangular Solid: (box)
- the union of a prism
whose bases and lateral faces are rectangles and the space it encloses
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/rectsold.gif)
- Reference angle:
- an acute in the first
quadrant, with the vertex at the origin, which is used to determine
the trigonometric functions of angles in the other quadrants
- Reflection:
- the image created
by flipping a point (or set of points) over a line to a new position
on the opposite side of the line, as if looking in a mirror
see also: transformations
- Regular (when
used in the name of a surface):
- adjective indicating
that the base(s) is a regular polygon; a regular prism or pyramid
is also right
- Regular polygon:
- a convex polygon that is both equilateral and equiangular
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/regpolyg.gif)
- Regular Pyramid:
- a pyramid that has a regular polygon for a
base, and whose altitude has
endpoints at the pyramid's vertex and at the center of the base
- Remote interior angles:
- the angles in a triangle that are not adjacent
to a given exterior angle
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/remextan.gif)
- Rhombus:
- a parallelogram with four equal sides; a square is a
special type of rhombus
- Right (when used
in the name of a surface):
- adjective indicating
either that the parallel bases
are aligned (for prisms and cylinders), or that the tip is centered
over the base (for pyramids and cones); a right
prism will have rectangular lateral faces; a right pyramid will
have lateral faces, which are isosceles
triangles
- Right angle:
- an angle whose measure is 90°
- Right cone:
- a cone in which the
endpoints of the altitude are the vertex and the center of the base
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/rtcone.gif)
- Right cylinder:
- a cylinder whose axis
is also an altitude
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/rtcylind.gif)
- Right prism:
- a prism in which the lateral surfaces are perpendicular
to the bases
- Right triangle:
- a triangle in which one of the angles measures 90°
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/rttriang.gif)
- Rotation:
- a figure is rotated
if every point moves through a given number of degrees around a
given point; (a rotation is an example of a rigid transformation)
a rotation is also defined as composition of two reflections over
intersecting lines of reflection
|
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/rectsold.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/regpolyg.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/remextan.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/rtcone.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/rtcylind.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/rttriang.gif)





