Geometry
Glossary - A
- Absolute Value:
- the distance a number
is from zero on the real number line; the absolute value of x, denoted
|x|, is equal to x if x
 0 and |x|=-x if x < 0
0 and |x|=-x if x < 0
- Acute angle:
- an angle having a measure
between 0° and 90°
-
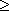
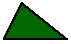
- Acute
triangle:
- a triangle which is
neither obtuse nor right;
in other words, its angles are all acute
- Adjacent Angles:
- a pair of angles that
share a vertex and a side, but no interior points
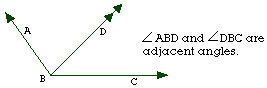
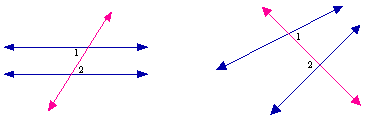
- Alternate Exterior
Angles:
- pairs of these angles
occur when two lines are intersected by a transversal; they are
located on opposite sides of the transversal on the "outside" of
the intersected lines
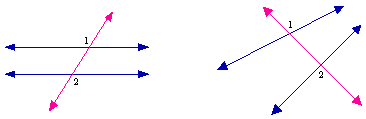
- Alternate Interior
Angles:
- pairs of these angles
occur when two lines are intersected by a transversal; they are
located on opposite sides of the transversal on the "inside" of
the intersected lines
- Altitude: (height)
- the distance between
the "top" and "bottom" of a figure
Altitude of a parallelogram:
a perpendicular to a pair of parallel sides
-
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/altparal.gif)
- Altitude of a Prism
or Cylinder:
- a segment perpendicular
to the parallel bases;
if the prism is right, then any lateral edge is congruent
to the altitude;
if the prism is oblique, then the
altitude may connect one base to the plane containing the other
base
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/altprism.gif)
- Altitude of a Pyramid
or Cone:
- a perpendicular
segment connecting the tip of the pyramid
(or cone) to the plane containing its
base;
if the pyramid (cone)
is oblique, the altitude may lie
outside the surface;
if the pyramid (cone) is right, the altitude connects the tip
to the center of the base
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/altpyra.gif)
- Altitude of a trapezoid:
- a perpendicular
to the two parallel sides
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/alttrap.gif)
- Altitude of a triangle:
- a perpendicular
from a vertex to its opposite
side
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/alttrian.gif)
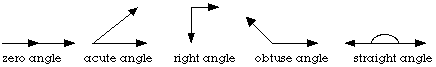
- Angle:
- the union of two rays
(or segments), which meet at an endpoint (called the vertex);
angles may be classified as acute, right, or obtuse (some sources
include straight angles that measure 180° and zero angles that
measure 0°)
- Antilogarithm:
- the number corresponding
to a base raised to a logarithmic
power
- Apothem:
- in a regular polygon,
it is the distance from the center to a side
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/apothem.gif)
- Arc:
- the portion of a curve
(usually of a circle) between and
including the two points on the curve
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/arc.gif)
- Area:
- the number of
square units covering the interior region of a closed plane figure
- Asymptote:
- a line that is approached
by a graph, but never touched by the graph
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/asymptot.gif)
- Axes:
- the horizontal (x-axis)
and vertical (y-axis) lines dividing the coordinate
plane into four quadrants
|
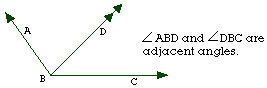



![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/apothem.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/arc.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/asymptot.gif)






 0 and |x|=-x if x < 0
0 and |x|=-x if x < 0![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/altparal.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/altprism.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/altpyra.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/alttrap.gif)
![[IMAGE]](../../genimage/glossimages/alttrian.gif)